[问答题]
A、B为两事件,P(A)=0.5,P(A-B)=0.2,则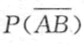 =().
=().
参考答案与解析:
-
相关试题
-
设A、B为两随机事件,P(A)=0.7,P(A-B)=0.3,则<img border="0" style="width: 55px; height: 23px;&
-
[单选题]设A、B为两随机事件,P(A)=0.7,P(A-B)=0.3,则=( )。[2008年真题]A.0.4B.0.5C.0.6D.0.7
- 查看答案
-
设A、B为随机事件,P(A)=0.7,P(A-B)=0.3,则<img border="0" style="width: 49px; height: 27px;&q
-
[单选题]设A、B为随机事件,P(A)=0.7,P(A-B)=0.3,则=()。A.0.3B.0.4C.0.6D.0.7
- 查看答案
-
设A、B为随机事件,P(A)=0.7,P(A-B)=0.3,则<img border="0" style="width: 49px; height: 27px;&q
-
[单选题]设A、B为随机事件,P(A)=0.7,P(A-B)=0.3,则=()。A.0.3B.0.4C.0.6D.0.7
- 查看答案
-
事件A与B互斥,P(A)=0.4,P(B)=0.3,则P(<img border="0" style="width: 35px; height: 24px;&quo
-
[单选题]事件A与B互斥,P(A)=0.4,P(B)=0.3,则P()=____.( )A.0.3B.0.42C.0.12D.0.7
- 查看答案
-
事件A与B互斥,P(A)=0.4,P(B)=0.3,则P(<img border="0" style="width: 36px; height: 22px;&quo
-
[单选题]事件A与B互斥,P(A)=0.4,P(B)=0.3,则P()=___.( )A.0.3B.0.42C.0.12D.0.7
- 查看答案
-
A、B为两个事件,P(A)≠P(B)>0,且A<img border="0" style="width: 24px; height: 23px;"
-
[单选题]A、B为两个事件,P(A)≠P(B)>0,且AB,则一定有( )A.P(AB)=1B.P(BA)=1C.P(B)=1D.P(A)=0
- 查看答案
-
A、B为两事件,若已知P(A)=0.92,P(B)=0.93,P(B|<img border="0" style="width: 29px; height: 37p
-
[问答题]A、B为两事件,若已知P(A)=0.92,P(B)=0.93,P(B|)=0.85.求:(1)P(AB);(2)P(A∪B).
- 查看答案
-
<img border="0" style="width: 44px; height: 44px;" src="https://img.zhao
-
[单选题]A.0.5kN·m,上侧受拉B.0.5kN·m,下侧受拉C.1kN·m,上侧受拉D.1kN·m,下侧受拉
- 查看答案
-
设事件A、B互不相容,且P(A)=p,P(B)=q,则<img border="0" style="width: 48px; height: 25px;"
-
[单选题]设事件A、B互不相容,且P(A)=p,P(B)=q,则=( )。A.q(1-p)B.qC.0D.p-q
- 查看答案
-
设事件A、B互不相容,且P(A)=p,P(B)=q,则<img border="0" style="width: 48px; height: 25px;"
-
[单选题]设事件A、B互不相容,且P(A)=p,P(B)=q,则=( )。A.q(1-p)B.qC.0D.p-q
- 查看答案
